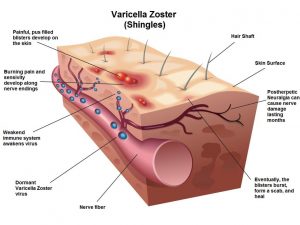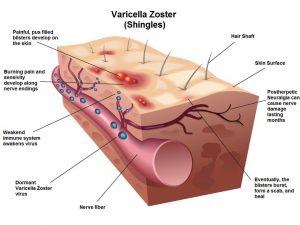
Who might be at greater risk of getting shingles?
- Do you have medical conditions that keep their immune systems from working properly, such as certain cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and
- receive immunosuppressive drugs, such as steroids and drugs that are given after organ transplantation.
HOW SHINGRIX WORKS… SHINGRIX boosts your body’s protection against shingles. Your immune system declines as you age, putting a person at an increased risk for shingles. For those who are 50 years and older, SHINGRIX helps your immune system defend against shingles. SHINGRIX is a 2-dose vaccine series (0.5 mL each) administered as an injection into the muscle in the upper arm. It is important to complete the 2‑dose series to help prevent shingles. Pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site, muscle pain, tiredness, headache, shivering, fever, and upset stomach are all common side effects of SHINGRIX.
SHINGRIX is the first shingles vaccine approved by the FDA in more than 10 years.
SHINGRIX is the only shingles vaccine proven to be up to 90% effective in clinical trials.